Blog
Jewellok is a professional pressure regulator and valve manufacturer and supplier.
About the Working Principle and Wide Application of Gas Solenoid Valve
- Pressure Regulator Valve Manufacturer
- 1/4 VCR Stainless Steel Ultra High Purity Gas Regulator, adjust gas valve pressure, application of ultra-high purity gas pressure regulator, Best high purity gas valve manufacturers in china, best high-pressure gas valve, best high-pressure gas valve suppliers, Best specialty gas valves manufacturers china, Best Ultra-High Purity Specialty Gases, China Gas Valve Manufacturers, China high purity gas valve manufacturer, China High purity gas valves manufacturers, China Industrial Gas Valve Manufacturer, China specialty gas valves manufacturers, China Ultra High Pressure Fittings Manufacturers, China Ultra High Purity Fittings Factory, China Ultra High Purity Gas Cylinder Valves, china ultra high purity gas regulator manufacturer, CNG gas valve, Custom Ultra High Purity Gas Delivery Solution, Diaphragm Valves for Ultra High-Purity Gas Systems, Dual stage ultra high purity gas regulators, Dual stage ultra high purity gas regulators Korea, Dual-Stage Ultra-High Purity Regulator, Gas Solenoid Valve, gas solenoid valve factory, gas solenoid valve manufacturer, gas solenoid valve supplier, gas valve, gas valve manifold box, Gas valve manufacturing in India, high pressure gas valve, high pressure gas valve manufacturer in turkey, high pressure gas valve supplier, Malaysia Ultra High Purity Gas Delivery Systems, Modular gas flow systems, OEM Ultra High Purity Gas Manufacturer, Premium gas systems for Ultra High Purity gases, Single Stage Compact Regulator for Ultra High Purity, Single Stage Regulator for Ultra High Purity, single stage ultra high purity nitrogen regulator
- No Comments
About the Working Principle and Wide Application of Gas Solenoid Valve
In the world of fluid control systems, gas solenoid valves play a pivotal role in ensuring safety, efficiency, and precision. These electromechanical devices are designed to control the flow of gases in various industrial, commercial, and residential applications. From regulating fuel supply in heating systems to managing gas flow in industrial processes, gas solenoid valves are indispensable components that combine reliability with automation. This article explores the intricacies of gas solenoid valves, delving into their working principles, types, applications, advantages, and considerations for selection and maintenance.

What is a Gas Solenoid Valve?
A gas solenoid valve is an electromechanical device that controls the flow of gas through a pipeline or system. It operates using an electromagnetic solenoid coil, which, when energized, moves a plunger or armature to open or close the valve, thereby allowing or stopping the flow of gas. These valves are widely used in systems requiring precise control, such as natural gas pipelines, propane systems, HVAC units, and industrial gas burners.
The primary function of a gas solenoid valve is to provide automated and remote control of gas flow, ensuring safety by preventing leaks and enabling rapid shutoff in emergencies. Unlike manual valves, solenoid valves can be integrated into automated systems, making them ideal for applications where real-time response and reliability are critical.
How Gas Solenoid Valves Work
The operation of a gas solenoid valve is based on the principles of electromagnetism. The valve consists of several key components:
- Solenoid Coil: An electromagnetic coil that generates a magnetic field when an electric current passes through it.
- Plunger or Armature: A movable component that responds to the magnetic field, opening or closing the valve.
- Valve Body: The housing that contains the gas flow path and sealing mechanism.
- Seals and Diaphragms: Components that ensure a tight seal to prevent gas leaks.
When the solenoid coil is energized, it creates a magnetic field that pulls or pushes the plunger, opening the valve to allow gas to flow. When the coil is de-energized, a spring or the pressure of the gas returns the plunger to its original position, closing the valve and stopping the flow. This rapid on-off mechanism makes gas solenoid valves highly efficient for applications requiring precise control.
Gas solenoid valves are typically classified as either normally closed (NC) or normally open (NO):
- Normally Closed (NC): The valve remains closed when de-energized and opens only when the solenoid is powered. This is the most common type for safety-critical applications, as it prevents gas flow in the event of power failure.
- Normally Open (NO): The valve remains open when de-energized and closes when the solenoid is powered. This type is used in applications where continuous gas flow is desired unless actively interrupted.
Types of Gas Solenoid Valves
Gas solenoid valves come in various designs to suit different applications. The main types include:
- Direct-Acting Solenoid Valves
These valves rely solely on the electromagnetic force of the solenoid to open or close the valve. They are simple, reliable, and suitable for low-pressure applications. Direct-acting valves are ideal for small-scale systems, such as residential gas appliances, due to their compact size and quick response time. - Pilot-Operated Solenoid Valves
Pilot-operated valves use the pressure of the gas itself to assist in opening or closing the valve. A small pilot valve controls the flow of gas to a diaphragm or piston, which then opens or closes the main valve. These valves are suitable for high-pressure or high-flow applications, such as industrial gas pipelines, as they require less electrical power to operate. - Two-Way Solenoid Valves
Two-way valves have one inlet and one outlet, making them suitable for simple on-off control of gas flow. They are commonly used in applications like gas burners and heating systems. - Three-Way Solenoid Valves
Three-way valves have three ports and are used to divert gas flow between two different paths or to mix gases from two sources. These valves are often found in complex systems requiring precise flow direction control, such as in HVAC systems or industrial processes. - Proportional Solenoid Valves
Unlike standard on-off solenoid valves, proportional valves can modulate the flow of gas by varying the electrical input to the solenoid. This allows for precise control of gas flow rates, making them ideal for applications like gas mixing or combustion control.
Applications of Gas Solenoid Valves
Gas solenoid valves are used across a wide range of industries and applications due to their versatility and reliability. Some key applications include:
- Industrial Processes
In industries such as oil and gas, chemical manufacturing, and food processing, gas solenoid valves regulate the flow of gases like nitrogen, oxygen, or natural gas. They are used in processes such as gas purging, burner control, and pressure regulation. - Heating Systems
Gas solenoid valves are critical components in residential and commercial heating systems, including boilers, furnaces, and water heaters. They control the supply of natural gas or propane to the burner, ensuring safe and efficient operation. - HVAC Systems
In heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, gas solenoid valves manage the flow of refrigerants or fuel gases, contributing to temperature control and energy efficiency. - Medical and Laboratory Equipment
In medical and laboratory settings, gas solenoid valves are used to control the flow of gases like oxygen, carbon dioxide, or anesthesia gases. Their precision and reliability are crucial for patient safety and experimental accuracy. - Automotive and Transportation
In automotive applications, gas solenoid valves regulate fuel flow in compressed natural gas (CNG) or liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) vehicles. They are also used in emissions control systems to manage exhaust gases. - Safety Systems
Gas solenoid valves are integral to safety systems, such as gas leak detection and shutoff systems. In the event of a detected leak or system malfunction, the valve can automatically close to prevent hazardous gas release.
Advantages of Gas Solenoid Valves
Gas solenoid valves offer several benefits that make them a preferred choice in many applications:
- Automation and Remote Control: Solenoid valves can be integrated into automated systems, allowing for remote operation and precise control via electrical signals.
- Rapid Response Time: These valves open and close quickly, making them ideal for applications requiring fast shutoff or flow adjustment.
- Safety: Normally closed solenoid valves enhance safety by automatically stopping gas flow in the event of power loss or system failure.
- Compact Design: Their small size makes them suitable for applications with limited space, such as residential appliances or portable equipment.
- Energy Efficiency: Solenoid valves consume minimal power, especially pilot-operated models, making them cost-effective for continuous operation.
- Versatility: Available in various materials, sizes, and configurations, gas solenoid valves can be tailored to suit specific gases, pressures, and environmental conditions.
Challenges and Considerations
While gas solenoid valves are highly reliable, certain challenges and considerations must be addressed when selecting and using them:
- Material Compatibility: The valve material must be compatible with the gas being controlled to prevent corrosion or degradation. For example, valves handling corrosive gases like ammonia may require stainless steel or specialized coatings.
- Pressure and Flow Requirements: The valve must be sized correctly to handle the system’s pressure and flow rate. Undersized or oversized valves can lead to inefficiencies or malfunctions.
- Power Supply: Solenoid valves require a stable electrical supply to operate. In areas with frequent power outages, backup systems or manual overrides may be necessary.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance is essential to ensure proper operation, especially in dusty or humid environments where debris or moisture can affect performance.
- Temperature Limitations: Some solenoid valves have temperature limitations, and exposure to extreme heat or cold can affect their performance or lifespan.
Selecting the Right Gas Solenoid Valve
Choosing the appropriate gas solenoid valve for a specific application requires careful consideration of several factors:
- Type of Gas: The valve must be compatible with the gas being controlled, whether it’s natural gas, propane, oxygen, or a corrosive gas.
- Pressure and Flow Rate: The valve must be rated for the system’s operating pressure and flow requirements.
- Valve Type: Decide between direct-acting, pilot-operated, two-way, three-way, or proportional valves based on the application’s needs.
- Environmental Conditions: Consider factors like temperature, humidity, and exposure to dust or chemicals when selecting materials and designs.
- Electrical Specifications: Ensure the valve’s voltage and power requirements match the system’s electrical setup.
- Certifications and Standards: For safety-critical applications, choose valves that meet industry standards, such as those set by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) or the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
To ensure the longevity and reliability of gas solenoid valves, regular maintenance is crucial. Key maintenance practices include:
- Inspection: Regularly check for signs of wear, corrosion, or leaks in the valve body and seals.
- Cleaning: Remove debris or contaminants that may accumulate in the valve, especially in dusty environments.
- Testing: Periodically test the valve’s operation to ensure it opens and closes correctly.
- Lubrication: If applicable, lubricate moving parts to reduce friction and wear.
- Electrical Checks: Verify that the solenoid coil and electrical connections are functioning properly.
Common issues with gas solenoid valves include failure to open or close, leaks, or erratic operation. These problems can often be traced to:
- Power Issues: Insufficient voltage or damaged wiring can prevent the solenoid from operating.
- Blockages: Debris or contaminants in the valve can obstruct the flow path or prevent proper sealing.
- Worn Components: Over time, seals, diaphragms, or springs may wear out and require replacement.
- Coil Failure: A burned-out or damaged solenoid coil can render the valve inoperable.
Future Trends in Gas Solenoid Valves
Advancements in technology are driving innovations in gas solenoid valves. Some emerging trends include:
- Smart Valves: Integration with IoT (Internet of Things) systems allows for remote monitoring, diagnostics, and predictive maintenance of solenoid valves.
- Energy-Efficient Designs: Newer valves are being designed to consume less power, reducing operational costs and environmental impact.
- Miniaturization: Compact solenoid valves are being developed for applications in portable devices and space-constrained systems.
- Enhanced Materials: Advances in materials science are leading to valves that can withstand harsher environments and more corrosive gases.

Conclusion
Gas solenoid valves are critical components in a wide range of applications, offering precise control, safety, and automation. From industrial processes to residential heating systems, these valves ensure efficient and reliable gas flow management. By understanding their working principles, types, applications, and maintenance requirements, users can select the right valve for their needs and ensure optimal performance. As technology continues to evolve, gas solenoid valves are becoming smarter, more efficient, and more versatile, solidifying their role as indispensable tools in modern fluid control systems.
For more about the working principle and wide application of gas solenoid valve, you can pay a visit to Jewellok at https://www.jewellok.com/ for more info.
Recent Posts
Five Key Considerations When Choosing a TMA Gas Changeover Manifold
How to Prevent Contamination in High Purity Xenon Gas Systems
Regulators for High Purity Krypton in Laser and Lighting Applications
Tags
Recommended Products
-
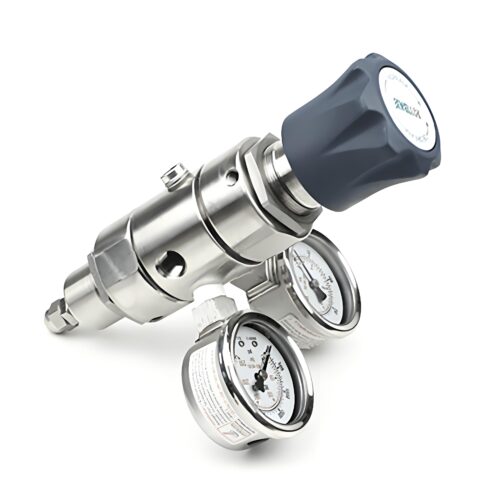

DPR1 Ultra High Purity Two Stage Dual Stage Pressure Reducing Regulator Semiconductor Grade Regulators
-
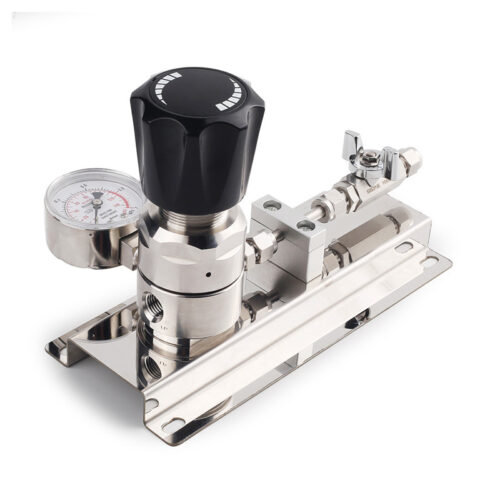

Ultra High Purity Stainless Steel Compressed Gas Changeover Manifold Panel System For Integrated Gas Supply System
-
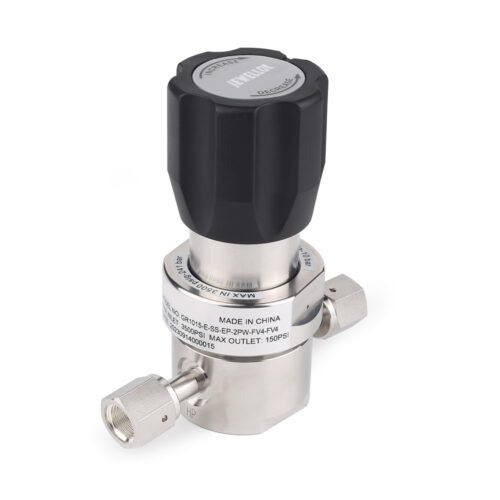

JR1000 Series UHP Ultra High Purity Single Stage Pressure Reducing Regulator And Low To Intermediate Flow
-

Long Gland LG Series For Ultra High Purity Gas And Chemical Delivery Systems
-

BSGS Large Flow Specialty Gas Supply Cabinet 3 Cylinder Gas Storage Cabinet Fully Automated PLC Control Bulk Specialty Gas Systems (BSGS) Gas Cabinets
-

High Purity Bulk Specialty Gas Pressure Control And Filtration Bulk Gas Skid Systems JW-300-BSGS
-

771LF Female Run Tee | Stainless Steel Tube Fitting Compression Fittings 1/4 In 3-Way Tee Female Run Tee
-

767LP Port Connector Ultra High Purity VCR Metal Gasket Face Seal Tube Fittings