Blog
Jewellok is a professional pressure regulator and valve manufacturer and supplier.
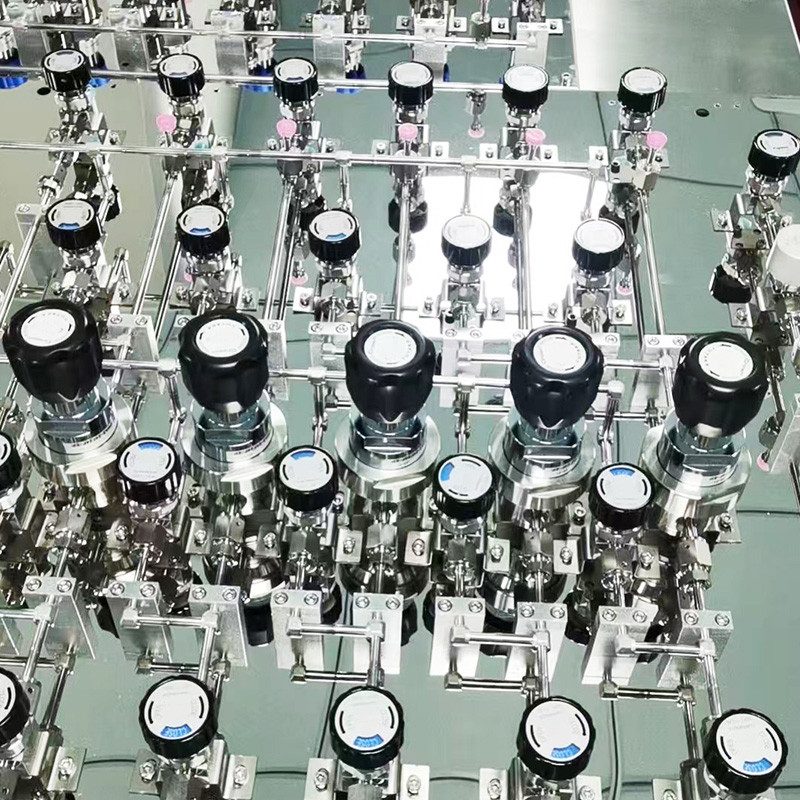
Can a High Purity Gas Regulator Be Customized?
- Pressure Regulator Valve Manufacturer
- 1/4 VCR Stainless Steel Ultra High Purity Gas Regulator, China High purity gas regulator Manufacturer, china ultra high purity gas regulator manufacturer, Dual stage ultra high purity gas regulators, Dual stage ultra high purity gas regulators Korea, dual-stage ultra-high purity gas regulator, high purity gas delivery systems, high purity gas regulator, high purity gas regulator in philippines, High purity gas regulator Manufacturer, High purity gas regulator Manufacturer china, high purity gas regulator manufacturer in china, high purity gas regulator manufacturer in india, high purity gas regulator manufacturer in korea, high purity gas regulator manufacturer in malaysia, high purity gas regulator manufacturer in taiwan, high purity gas regulator manufacturer in thailand, High Purity Gas Regulator Max In 400 Max out 250 psi, high purity gas regulator supplier, high purity gas regulator thailand, laboratory High Purity Gas Regulator, Laboratory high purity gas regulator manual, Ultra High Purity Gas Cylinder Valves, Ultra High Purity Gas Valves, Ultra high purity gas valves china, ultra high purity gas valves in brazil, Ultra high purity gas valves manufacturer, ultra high purity gas valves thailand
- No Comments
Can a High Purity Gas Regulator Be Customized?
Introduction
In the realm of industrial and scientific applications, high purity gas regulators play a pivotal role in ensuring the precise control and delivery of gases while maintaining their integrity against contamination. These devices are essential in sectors such as semiconductor manufacturing, pharmaceutical production, analytical laboratories, and biotechnology, where even trace impurities can compromise processes, leading to costly failures or safety hazards. A high purity gas regulator is designed to handle gases like nitrogen, oxygen, helium, or specialty mixtures at purity levels often exceeding 99.999%, minimizing the introduction of particulates, moisture, or other contaminants.
The question of whether such regulators can be customized is not merely academic; it addresses the practical needs of engineers and technicians who must adapt equipment to specific operational demands. The short answer is yes—high purity gas regulators can indeed be customized extensively. This customization allows for tailoring to unique environmental conditions, pressure requirements, flow rates, and compatibility with various gas types. However, the process involves careful consideration of materials, design standards, and regulatory compliance to preserve the regulator’s performance and safety.
This article delves into the technical aspects of high purity gas regulators, explores the feasibility and methods of customization, discusses key customizable features, outlines the customization process, examines benefits and potential challenges, and concludes with insights into emerging trends. By understanding these elements, professionals can make informed decisions on whether customization is the right path for their applications.

Understanding High Purity Gas Regulators
To appreciate the scope of customization, it’s essential to first grasp the fundamental design and function of high purity gas regulators. At their core, these regulators reduce the pressure of gas from a high-pressure source, such as a cylinder or pipeline, to a lower, usable level while maintaining a stable outlet pressure. Unlike standard regulators, high purity versions incorporate features to prevent contamination.
Key components include:
– Body and Wetted Parts: Typically constructed from electropolished stainless steel (e.g., 316L grade) or exotic alloys like Hastelloy or Monel to resist corrosion and minimize particle shedding.
– Diaphragm or Piston: Acts as the sensing element. In high purity designs, tied-diaphragm configurations are common to eliminate potential leak paths.
– Seats and Seals: Made from materials like PTFE, PCTFE, or Viton, chosen for their inertness and low outgassing properties.
– Inlet and Outlet Connections: Often featuring VCR (Vacuum Coupling Radiation) or face-seal fittings to ensure leak-tight connections.
– Gauges and Valves: Integrated or optional, with helium leak-tested assemblies to achieve leak rates below 10^-9 atm-cc/sec.
These regulators operate on principles of pressure balance, where inlet pressure acts against a spring-loaded diaphragm to control flow. For ultra-high purity applications, they may include diffusion-resistant barriers or helium-purged enclosures.
Standard off-the-shelf regulators suffice for many uses, but customization becomes necessary when dealing with aggressive gases (e.g., chlorine or hydrogen fluoride), extreme temperatures (-196°C for cryogenics to 200°C for heated processes), or specialized flow dynamics.
Why Customize a High Purity Gas Regulator?
Customization arises from the diversity of applications. In semiconductor fabrication, for instance, regulators must handle ultra-pure argon for plasma etching without introducing silicon or metal contaminants. In pharmaceutical cleanrooms, they deliver sterile air or nitrogen compliant with USP (United States Pharmacopeia) standards. Laboratories might require regulators for gas chromatography that maintain sub-ppm impurity levels.
Off-the-shelf models often fall short in scenarios involving:
– Non-Standard Pressure Ranges: Default inlet pressures might be 3000 psig, but custom needs could extend to 6000 psig for high-pressure cylinders.
– Unique Gas Compatibilities: Corrosive gases demand specific alloys to prevent degradation.
– Integration with Systems: Custom mounting brackets or manifold integrations for multi-gas setups.
– Environmental Factors: Operation in hazardous areas (e.g., ATEX-certified for explosive atmospheres) or under vacuum conditions.
Customization ensures optimal performance, enhances safety, and can reduce long-term costs by preventing downtime from mismatched equipment.
Key Customizable Aspects
High purity gas regulators offer a wide array of customization options, categorized into mechanical, material, functional, and accessory modifications.
Material Selection
Materials are paramount for purity maintenance. Standard bodies use 316L stainless steel with a surface finish of 10 Ra or better via electropolishing. Customization might involve:
– Exotic Alloys: Hastelloy C-22 for chlorine service, reducing pitting corrosion.
– Coatings: Ceramic or diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings on internal surfaces to minimize friction and particle generation.
– Elastomers: Switching from Viton to Kalrez for better chemical resistance in fluorinated gas applications.
These choices are guided by compatibility charts and finite element analysis (FEA) to predict material behavior under stress.
Pressure and Flow Configurations
Regulators can be tuned for specific pressure drops and flow coefficients (Cv). For example:
– Inlet/Outlet Pressures: Custom ranges from vacuum to 10,000 psig inlet, with outlet stability within ±0.1% of setpoint.
– Flow Rates: Adjusting orifice sizes or adding flow restrictors for Cv values from 0.02 (low flow) to 1.0 (high flow).
– Multi-Stage Designs: For applications requiring ultra-stable outlet pressure, a two-stage regulator can be customized with intermediate relief valves.
Connection Types
Standard connections like NPT or CGA are common, but customization includes:
– Ultra-High Purity Fittings: VCR, VCO, or Swagelok-compatible for zero-dead-volume connections.
– Custom Ports: Additional gauge ports or vent lines for pressure monitoring.
– Manifold Assemblies: Integrating multiple regulators into a single panel for gas mixing stations.
Safety and Control Features
Enhancing safety through:
– Pressure Relief Devices: Custom burst disks set to specific rupture pressures.
– Lockout Mechanisms: Tamper-proof adjustments for regulated environments.
– Electronic Integration: Adding transducers for 4-20 mA output signals, enabling SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) compatibility.
– Filtration: Incorporating sintered metal filters with 0.1-micron ratings to capture upstream contaminants.
Aesthetic and Ergonomic Customizations
While less technical, these include color-coding for gas identification, custom labeling, or ergonomic knobs for glove-friendly operation in cleanrooms.
The Customization Process
Customizing a high purity gas regulator typically follows a structured engineering process:
- Needs Assessment: Collaborate with the manufacturer to define requirements via questionnaires covering gas type, pressure/flow specs, environmental conditions, and compliance needs (e.g., ASME, ISO 9001).
- Design Phase: Use CAD software to model the regulator. Simulations via CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) predict flow patterns and potential contamination risks.
- Material and Component Sourcing: Select and procure certified materials, often with traceability to mill certificates.
- Prototyping: Build a prototype, subjected to helium leak testing, pressure cycling (up to 10,000 cycles), and purity analysis using techniques like APIMS (Atmospheric Pressure Ionization Mass Spectrometry).
- Testing and Validation: Conduct burst tests, vibration resistance per MIL-STD-810, and compatibility immersion tests. For high purity, outgassing rates are measured under vacuum.
- Manufacturing and Quality Control: Assemble in ISO Class 5 cleanrooms, with each unit serialized and documented.
- Delivery and Support: Include installation guides, calibration certificates, and ongoing maintenance plans.
Lead times can range from 4-12 weeks, depending on complexity, with costs 20-50% higher than standard models.
Benefits of Customization
The advantages are multifaceted:
– Enhanced Performance: Tailored designs minimize pressure fluctuations, improving process yields in applications like CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition).
– Cost Efficiency: Preventative customization reduces failures; for example, a custom corrosion-resistant regulator avoids frequent replacements in acidic environments.
– Compliance and Safety: Meets specific standards like SEMI (Semiconductor Equipment and Materials International) guidelines, reducing liability.
– Scalability: Custom manifolds support expansion in growing facilities.
In a hypothetical semiconductor plant, customizing regulators for silane gas delivery prevented cross-contamination, boosting wafer production by 15%.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite benefits, challenges exist:
– Cost Implications: Higher upfront expenses and longer procurement times.
– Complexity: Over-customization can lead to reliability issues if not thoroughly tested.
– Supply Chain Dependencies: Rare materials may delay projects.
– Maintenance: Custom parts might require specialized servicing.
Key considerations include budgeting for lifecycle costs, partnering with reputable manufacturers, and conducting risk assessments using FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis).
Emerging Trends in Customization
Looking ahead, advancements are shaping customization:
– Smart Regulators: Integration with IoT for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance via AI algorithms.
– Additive Manufacturing: 3D printing of custom components for rapid prototyping and complex geometries.
– Sustainable Materials: Shift towards recyclable alloys and low-emission manufacturing.
– Modular Designs: Allowing field-upgradable modules for evolving needs.
These trends promise more agile and efficient customization, aligning with Industry 4.0 principles.

Conclusion
In summary, high purity gas regulators can be extensively customized to meet the demands of specialized applications, offering flexibility in materials, pressures, connections, and features. This capability not only enhances operational efficiency but also ensures safety and compliance in critical industries. While the process requires careful planning and investment, the long-term benefits often outweigh the challenges. As technology evolves, customization will become even more accessible, enabling innovations in gas handling systems. Professionals should evaluate their specific needs and consult experts to determine the optimal customization strategy.
For more about can a high purity gas regulator be customized, you can pay a visit to Jewellok at https://www.jewellok.com/product-category/ultra-high-purity-regulators/ for more info.
Recent Posts
The Inner Workings of a 316L VIM-VAR Stainless Steel Pressure Regulator
How Ultra-High Purity Stainless Steel Tubing Powers Critical Industries
How Does a UHP 316L Stainless Steel Bellows Valve Work?
How Does a 316 Stainless Steel Pipe Fitting Work?
A Comprehensive Guide to 316L VIM VAR UHP Gas Regulator
Tags
Recommended Products
-

Ultra High Purity Trimethylaluminum TMA Gas Cabinet Liquid Delivering Cabinet Used For Specialty Gas Delivery System In Semiconductor
-

High Purity And Industria Gas Stick Assemblies Precise Pressure Control Gas Systems JSR-1ETG-BV Series
-
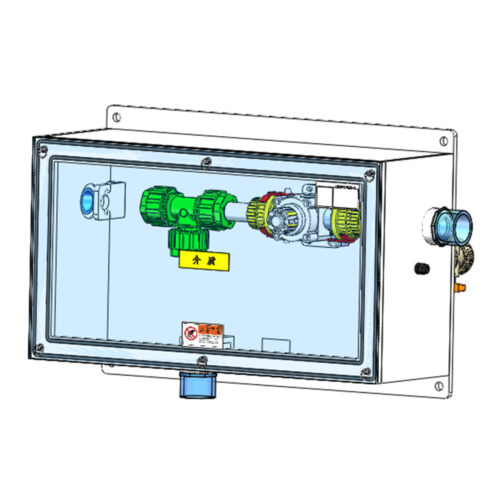
FT-BOX JW-FTB-C Valve Manifold Panels And Boxes With High Purity Configurable Systems
-

Stainless Steel Low Pressure Seal Pneumatic Diaphragm Control Valve For For HP & UHP Gases
-

Line And Panel Mounting Adjustable Low Pressure Propane And Nitrogen Pressure Regulator JSR-3L & JSR-3LP Series
-

Flow Control Stainless Steel Low Pressure Manual Diaphragm Valve For High Purity And Ultra High Purity Gases
-

771L Male Run Tee | Stainless Steel High Quality High Purity Male Run Tee Branch Tee Pipe Fittings
-

Medical Oxygen Single Stage Manual Gas Changeover Manifold Panel High-Purity Two-Stage Manual Gas Manifold Gas Pressure Control Panels