Blog
Jewellok is a professional pressure regulator and valve manufacturer and supplier.
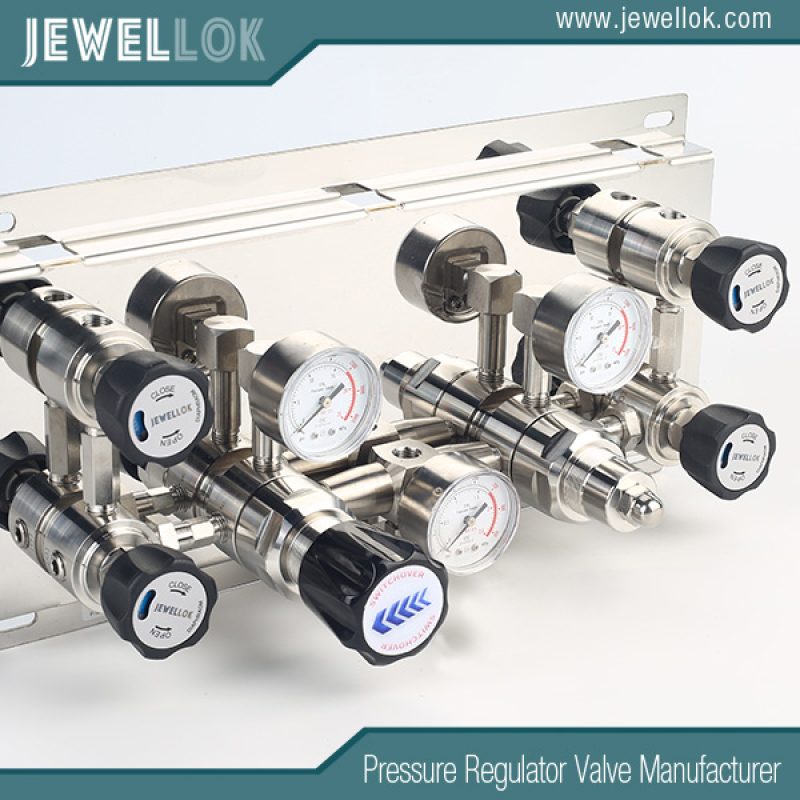

SiH4 Gas Manifold: Design, Applications, and Safety Considerations
- Pressure Regulator Valve Manufacturer
- Automatic gas changeover system, CVD process gas delivery, Emergency shutdown valves SiH4, Gas manifold design principles, Gas manifold maintenance protocols, Hazardous gas handling equipment, High-purity gas filtration, IoT smart gas manifolds, Leak detection in gas manifolds, Mass flow controllers for SiH4, Photovoltaic SiH4 manifold, Pyrophoric gas manifold, SEMI S2 compliance gas systems, Semiconductor gas manifold, SiH4 applications in semiconductors, sih4 gas manifold, SiH4 gas purity requirements, SiH4 handling safety, Sih4 Valve Manifold Box, Silane gas distribution system, stainless steel gas manifold
- No Comments
SiH4 Gas Manifold: Design, Applications, and Safety Considerations
In the realm of semiconductor manufacturing and advanced materials processing, silane (SiH4) plays a pivotal role as a precursor gas for depositing silicon-based films. SiH4, a colorless, pyrophoric gas with a distinctive odor, is highly reactive and flammable, making its handling a critical aspect of industrial operations. A SiH4 gas manifold serves as the central distribution system that ensures safe, efficient, and controlled delivery of this gas from storage cylinders to process equipment. This technical article delves into the intricacies of SiH4 gas manifolds, exploring their design principles, key components, operational mechanisms, applications, and essential safety protocols. By understanding these systems, engineers and technicians can optimize performance while mitigating risks associated with handling hazardous gases.
The importance of a well-engineered SiH4 gas manifold cannot be overstated. In high-purity environments like cleanrooms, where even minute contaminants can compromise product yields, the manifold acts as a gateway for gas flow. It regulates pressure, filters impurities, and provides redundancy to prevent downtime. As industries push toward smaller nanoscale features in electronics, the demand for precise SiH4 delivery systems has surged, driving innovations in manifold technology.
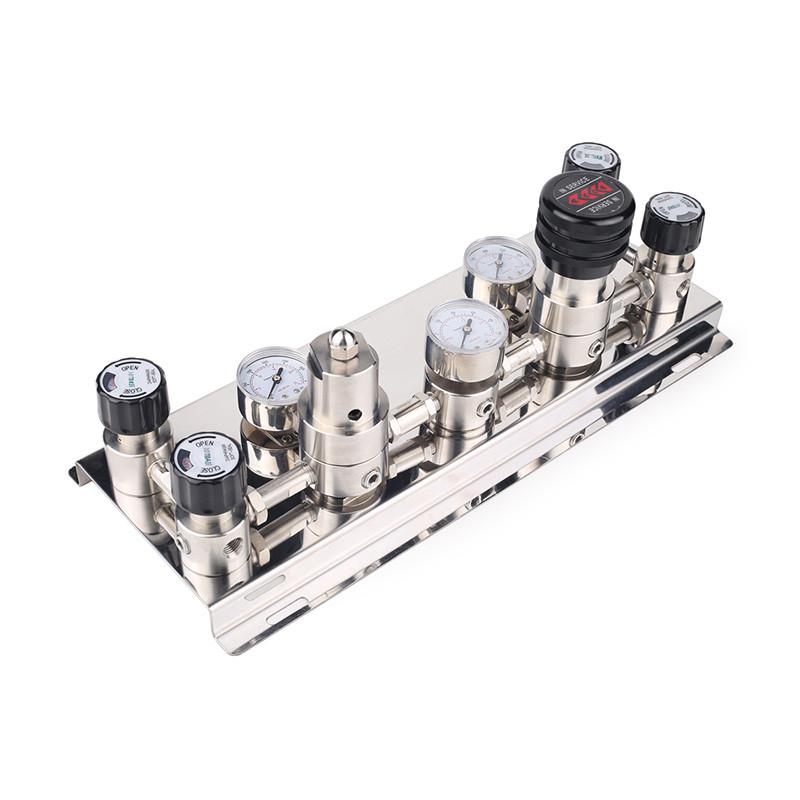

Design Principles of SiH4 Gas Manifolds
The design of a SiH4 gas manifold begins with material selection to withstand the gas’s corrosive and reactive nature. Typically, manifolds are constructed from high-grade stainless steel, such as 316L, which offers excellent resistance to corrosion and maintains ultra-high purity levels. Electropolishing of internal surfaces reduces particle generation and enhances cleanliness, crucial for semiconductor applications where purity exceeds 99.9999%.
A standard SiH4 gas manifold configuration includes multiple inlet ports for connecting gas cylinders, allowing for seamless switching between sources. This setup often employs automatic changeover systems that detect low pressure in one cylinder and switch to a backup without interrupting flow. Pressure regulators, made from materials compatible with SiH4, maintain downstream pressure within tight tolerances, usually between 0.5 to 5 bar, depending on the process requirements.
Flow control is achieved through mass flow controllers (MFCs) integrated into the manifold. These devices use thermal or pressure-based sensing to measure and adjust gas flow rates accurately, often down to milliliters per minute. For SiH4, which decomposes at elevated temperatures, manifolds incorporate cooling elements or insulation to prevent premature reactions. Additionally, purge lines with inert gases like nitrogen are essential to evacuate the system during cylinder changes, minimizing exposure to air and reducing the risk of ignition.
Modular designs have become prevalent, enabling scalability. A basic manifold might support two cylinders, while advanced systems can handle dozens, distributed across panels for space efficiency. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations are often used in the design phase to optimize gas paths, ensuring uniform distribution and minimal dead volumes where gas could stagnate and decompose.
Key Components and Functionality
At the heart of a SiH4 gas manifold are several critical components that work in concert. Cylinder connections utilize CGA (Compressed Gas Association) fittings specific to SiH4, such as CGA 350, to ensure leak-proof seals. Isolation valves, often pneumatically actuated, allow for sectional shutdowns during maintenance.
Filters and purifiers are integral to remove particulates and trace impurities. Point-of-use purifiers, employing getter materials, can achieve sub-ppb (parts per billion) purity levels for moisture and oxygen, which are detrimental to SiH4 stability. Pressure transducers and gauges provide real-time monitoring, feeding data to programmable logic controllers (PLCs) for automated control.
The manifold’s control system often integrates with supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) software, enabling remote monitoring and alarms for anomalies like pressure drops or leaks. In hazardous environments, explosion-proof enclosures house electrical components to comply with ATEX or NEC standards.
Functionally, the manifold operates in phases: supply, regulation, distribution, and exhaust. During supply, gas enters from cylinders under high pressure (up to 150 bar). Regulation reduces this to usable levels, while distribution routes it to multiple endpoints via stainless steel tubing. Exhaust systems, including scrubbers, neutralize any vented SiH4 to prevent environmental release.
Applications in Industry
SiH4 gas manifolds find extensive use in the semiconductor industry for chemical vapor deposition (CVD) processes. In plasma-enhanced CVD (PECVD), SiH4 is decomposed to form silicon dioxide or nitride layers in integrated circuits. Manifolds ensure consistent gas delivery, directly impacting film uniformity and device performance.
Beyond semiconductors, SiH4 is employed in photovoltaic manufacturing for amorphous silicon solar cells. Here, manifolds support large-scale deposition chambers, where flow rates can exceed several liters per minute. In the production of flat-panel displays, SiH4 manifolds facilitate the creation of thin-film transistors.
Emerging applications include nanotechnology and advanced ceramics, where SiH4 serves as a silicon source for nanowires or coatings. In research labs, compact manifolds enable precise experiments in materials science. The automotive sector also benefits indirectly, as SiH4-derived materials enhance sensor technologies.
In all these applications, the manifold’s reliability is paramount. Downtime in a fab can cost millions, so redundant designs with hot-swappable components are standard. Integration with Industry 4.0 principles allows predictive maintenance, using AI to forecast component failures based on usage data.
Safety Protocols and Maintenance
Handling SiH4 demands stringent safety measures due to its pyrophoric properties—it ignites spontaneously in air at concentrations above 1.4%. SiH4 gas manifolds incorporate multiple safety layers, starting with leak detection systems using infrared sensors or mass spectrometers to identify trace leaks.
Emergency shutdown valves (ESVs) activate upon detecting hazards, isolating the manifold. Ventilation systems maintain negative pressure in enclosures to contain any releases. Personal protective equipment (PPE) protocols, including self-contained breathing apparatus, are mandatory for operators.
Maintenance of SiH4 gas manifolds follows a rigorous schedule. Daily visual inspections check for leaks or corrosion, while weekly calibrations verify MFC accuracy. Annual overhauls involve dismantling, cleaning with inert solvents, and replacing seals. Helium leak testing ensures integrity post-maintenance.
Training is crucial; personnel must understand SiH4’s hazards, including its potential to form explosive mixtures. Compliance with standards like SEMI S2 for semiconductor equipment safety guides manifold operations.
Environmental considerations include proper disposal of spent cylinders and scrubber effluents. Recycling programs for SiH4 cylinders reduce waste, aligning with sustainability goals.

Challenges and Future Trends
Despite advancements, challenges persist in SiH4 gas manifold technology. Miniaturization demands even higher purity and precision, pushing the limits of current materials. Cost pressures in competitive markets require balancing sophistication with affordability.
Future trends point toward smart manifolds with IoT integration for real-time analytics. Advances in 3D printing could enable custom manifold geometries, reducing lead times. Alternative gases or precursors might emerge, but SiH4’s established role ensures manifolds will evolve alongside.
In conclusion, the SiH4 gas manifold represents a cornerstone of safe and efficient gas handling in high-tech industries. Its design, components, and safety features underscore the blend of engineering prowess and risk management necessary for hazardous materials. As technology advances, these systems will continue to adapt, supporting innovations that drive modern electronics and beyond.
For more about sih4 gas manifold: design, applications, and safety considerations, you can pay a visit to Jewellok at https://www.specialtygasregulator.com/product-category/gas-changeover-system/ for more info.
Recent Posts
Key Specifications: UHP Argon Valves for 99.999% Purity Gas Systems
How to Select the Right Valve Manifold Box for Your Application
316L Stainless Steel Ultra High Purity Regulator for PH3 Service
How to Safely Operate a TMA Gas Changeover Manifold
Tags
Recommended Products
-

Stainless Steel High Purity High Temperature Pneumatic Actuated Ball Valves JBV2 Series
-

BSGS Large Flow Specialty Gas Supply Cabinet 3 Cylinder Gas Storage Cabinet Fully Automated PLC Control Bulk Specialty Gas Systems (BSGS) Gas Cabinets
-
Scrubber Tail Gas Treatment Cabinet Waste Gas Treatment Wet Scrubber Exhaust Gas Treatment Spray Tower
-

High Purity Semi-Auto Stainless Steel Changeover Manifold System, Nitrogen High Pressure Control Panel With Semiconductor Valve Manifold Box Diaphragm Valves
-

Stainless Steel Ultra Clean Welding Joint Fittings TW Series TRW Series & CW Series
-

Stainless Steel Mini Elbow Mini Tee Mini Cross Mini Tribow Ultrahigh Purity Mini Butt Weld Fittings
-

763L Stainless Steel High Purity Pressure Reducing Union Fittings And Tubing Pressure Reducing Valve Adjustment
-

Ultra High Purity Stainless Steel Compressed Gas Changeover Manifold Panel System For Integrated Gas Supply System