Blog
Jewellok is a professional pressure regulator and valve manufacturer and supplier.
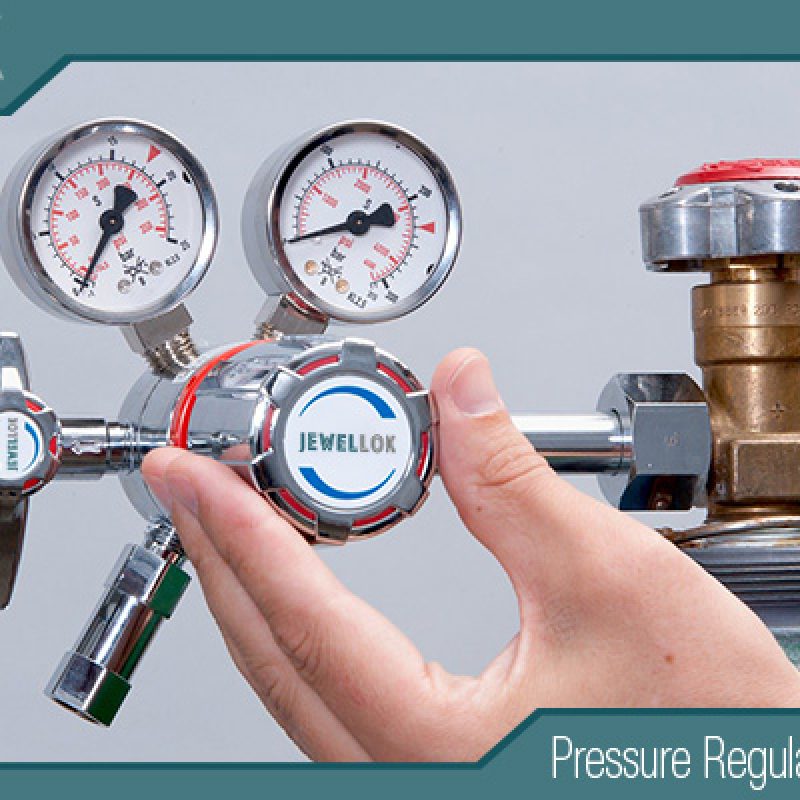
Safety Features of Gas Changeover Manifolds: Ensuring Operational Safety
- Pressure Regulator Valve Manufacturer
- 1 1 2 gas pressure regulator, 1 2 gas regulator, 1/2 gas pressure regulator, 1/4 VCR Stainless Steel Ultra High Purity Gas Regulator, 2-stage auto changeover lp propane gas regulator, 3/4 natural gas regulator, 316L Stainless Steel Gas Pressure Regulators, 4 Cylinder Gas Cabinet, 7000 series compressed gas cabinet, adjust gas valve pressure, Adjustable Helium Single Stage High Pressure Gas Regulator, adjustable natural gas regulator, application of ultra-high purity gas pressure regulator, argon gas changeover manifold, argon gas changeover manifold supplier, argon gas changeover manifold supplier philippines, Argon Gas Cylinder Storage Cabinet, Argon Gas Flow Gauge Regulator, Argon Gas Flow Gauge Regulator And Valves, Argon Gas Flow Gauge Valves, Fully Automatic Medical Gas Manifolds, gas changeover manifold, gas manifolds, Gas Manifolds Manufacturers and Suppliers in the USA, Gas Manifolds Manufacturers in India, Oil and Gas Manifolds, Specialty Gas Manifolds, Specialty Gas Manifolds China, Specialty Gas Manifolds Russia, Specialty Gas Manifolds Turkey
- No Comments
Safety Features of Gas Changeover Manifolds: Ensuring Operational Safety
Gas changeover manifolds are critical infrastructure in industries and facilities that rely on a continuous supply of compressed gases, such as hospitals, laboratories, manufacturing plants, chemical processing facilities, and welding operations. These systems automatically switch between gas cylinder banks when one depletes, ensuring uninterrupted flow without manual intervention. However, the true value of a gas changeover manifold lies in its safety features, which are designed to prevent accidents, leaks, over-pressurization, and contamination. Safety is paramount because gases like oxygen, hydrogen, or chlorine can be flammable, toxic, or life-sustaining, and any failure could lead to catastrophic consequences, including explosions, asphyxiation, or medical emergencies.This 2000-word article explores the key safety features of gas changeover manifolds, explaining how they work, their importance, and how they contribute to overall system reliability. We’ll also discuss regulatory standards, best practices for maintenance, real-world applications, and emerging trends in safety design. By understanding these features, facility managers, engineers, and safety officers can make informed decisions when selecting, installing, and operating manifolds to protect personnel, equipment, and the environment.

Understanding Gas Changeover Manifolds
Before diving into safety features, it’s essential to understand the basics of gas changeover manifolds. A gas changeover manifold is a centralized system that connects multiple gas cylinders (typically grouped into primary and reserve banks) to a single outlet line. It monitors pressure levels and automatically switches from the primary bank to the reserve when the primary depletes, ensuring continuous gas supply. Manifolds can be manual, semi-automatic, or fully automatic, with the latter being most common in high-stakes environments like hospitals.In hospitals, for instance, manifolds ensure a steady supply of medical gases such as oxygen, which is vital for patient care in operating rooms, ICUs, and respiratory therapy. According to the NFPA 99 standard, medical gas systems must incorporate safety features to prevent failures. Safety features are not optional add-ons; they are integral to the design, addressing risks like pressure buildup, gas leaks, contamination, and supply interruptions.Key Safety Features of Gas Changeover ManifoldsGas changeover manifolds incorporate multiple safety features to mitigate risks associated with high-pressure gases. These features are engineered to prevent accidents, ensure compliance, and maintain operational integrity. Let’s examine the most important ones in detail.
- Automatic Changeover Mechanism
The core safety feature of modern manifolds is the automatic changeover system, which detects low pressure in the active cylinder bank and seamlessly switches to the reserve bank. This prevents sudden gas supply interruptions, which could be life-threatening in hospitals (e.g., during surgery or ventilation).
- How It Works: Pressure sensors or transducers monitor cylinder pressure. When it drops below a preset threshold (e.g., 50-100 psi), the system activates a solenoid or mechanical valve to switch banks.
- Importance: Eliminates human error from manual switching and ensures continuous supply. In semi-automatic systems, it switches automatically but requires manual reset, while fully automatic versions handle everything.
- Example: The Pattons Medical manifold uses dome-loaded technology for fail-safe switching, free of fluoropolymers for added safety in high-pressure scenarios.
Expert Insight: This feature complies with NFPA 99, which mandates automatic changeover for medical gas systems to avoid supply failures.
- Pressure Relief Valves
Pressure relief valves (PRVs) are safety devices that automatically release excess pressure to prevent over-pressurization, which could cause cylinder rupture or leaks.
- How It Works: When pressure exceeds a set limit (e.g., 1.5 times the working pressure), the valve opens to vent gas safely, then reseats when pressure normalizes.
- Importance: Protects against pressure spikes from temperature changes or regulator failures, crucial for flammable gases like hydrogen or oxygen, which can ignite under pressure.
- Example: Amico’s NFPA-compliant manifolds include built-in PRVs on headers to safeguard the system.
Expert Insight: PRVs are required by standards like NFPA 55 for compressed gases, ensuring they vent to safe locations to avoid hazardous accumulation.
- Check Valves
Check valves prevent backflow of gas from one cylinder bank to another or from the outlet to the inlet, avoiding contamination or pressure imbalances.
- How It Works: A one-way mechanism (e.g., ball or flap) allows flow in one direction but closes against reverse flow.
- Importance: Prevents mixing of incompatible gases (e.g., oxygen and acetylene) or reverse contamination, reducing explosion or corrosion risks.
- Example: Genstar Technologies’ manifolds include check valves in pigtails to ensure safe cylinder replacement.
Expert Insight: Check valves are vital for compliance with CGA standards, which emphasize preventing backflow in high-purity systems.
- Audible and Visual Alarms
Alarms notify operators of low pressure, changeover events, or system faults, allowing timely intervention.
- How It Works: Pressure switches trigger alarms (buzzers, lights, or digital alerts) when thresholds are met.
- Importance: In hospitals, alarms prevent gas shortages during critical care, potentially saving lives. They also signal maintenance needs, reducing downtime.
- Example: Middlesex Gases’ semi-automatic manifolds feature loud alarms for switchover, as noted in search results.
Expert Insight: NFPA 99 requires alarms for medical gas systems, with remote monitoring for 24/7 facilities.
- Purge Systems
Purge systems remove air, moisture, or residual gases from lines during cylinder changes, preventing contamination.
- How It Works: Vent valves or purge ports allow inert gas flushing before connecting new cylinders.
- Importance: Essential for high-purity gases (e.g., medical oxygen), where moisture can cause corrosion or contamination, leading to safety hazards.
- Example: Pattons Medical manifolds include HP vent valves for purging, ensuring clean lines.
Expert Insight: Purge features align with CGA G-4.1 for oxygen systems, minimizing fire risks from impurities.
- Safety Relief Valves and Burst Discs
These devices protect against extreme over-pressure by venting or rupturing at predetermined levels.
- How It Works: Relief valves open to release pressure, while burst discs rupture as a last resort.
- Importance: Prevents explosions in high-pressure systems, especially for compressed gases.
- Example: Airgas manifolds feature safety relief valves, as per industry standards.
Expert Insight: OSHA and NFPA mandate these for compressed gas systems to mitigate over-pressure risks.
- Isolation Valves
Isolation valves allow individual cylinders to be shut off for replacement without affecting the system.
- How It Works: Manual or automatic valves close flow from depleted cylinders.
- Importance: Enables safe cylinder changes while maintaining supply, reducing exposure risks.
- Example: CK Supply manifolds include isolation valves for each cylinder.
Expert Insight: This feature complies with NFPA 55, ensuring safe handling during maintenance.
- Filters and Particle Traps
Filters remove impurities like dust or moisture from gas lines.
- How It Works: Sintered metal or membrane filters trap particles.
- Importance: Prevents contamination in high-purity systems, reducing equipment failures or health risks in hospitals.
- Example: Jewell Instruments manifolds include filters for specialty gases.
Expert Insight: SEMI standards require filtration in UHP systems to maintain gas purity.
These features collectively make gas changeover manifolds safe and reliable.
Importance of Safety Features in Gas Changeover Manifolds
Safety features are not just add-ons—they are fundamental to preventing accidents and ensuring compliance. In hospitals, for example, a manifold failure could interrupt oxygen supply to ventilators, endangering patients. In industrial settings, leaks from flammable gases could cause explosions. Features like automatic changeover and alarms minimize human error, while relief valves and check valves mitigate physical risks. Overall, they protect lives, property, and the environment.
Regulatory Standards Governing Safety Features
Safety features in gas changeover manifolds are mandated by various standards:
- NFPA 99 (USA): Requires automatic changeover, alarms, and relief valves for medical gas systems.
- HTM 02-01 (UK): Specifies purge systems, isolation valves, and alarms for hospitals.
- ISO 7396: International standard for medical gas pipelines, emphasizing safety relief and check valves.
- CGA P-1: Guidelines for safe gas handling, including burst discs and filters.
- OSHA 1910.101: Ensures safe storage and handling, mandating ventilation and labeling.
- ASME B31.3: Governs process piping, requiring pressure testing and relief valves.
Compliance ensures manifolds meet safety thresholds, with certifications from bodies like UL or CE.
Installation and Safety Integration
Proper installation integrates safety features:
- Location: Ventilated, secure rooms with gas detection.
- Piping: Stainless steel with check valves.
- Alarms: Connected to central monitoring.
- Testing: Leak and pressure tests per NFPA.
Professional installation ensures all safety features function correctly.
Maintenance for Safety
Maintenance preserves safety features:
- Daily Checks: Monitor pressure and alarms.
- Monthly: Inspect valves and filters.
- Annual: Calibrate sensors, test relief valves.
- Cylinder Handling: Follow CGA guidelines to avoid damage.
Regular maintenance prevents failures and ensures compliance.
Case Studies: Safety Features in Action
- Hospital in USA: A fully automatic manifold with alarms and relief valves prevented oxygen shortage during a cylinder depletion, saving lives per NFPA 99.
- Chemical Plant in Germany: Check valves and purge systems prevented contamination from backflow, avoiding an explosion.
- Laboratory in UK: Pressure relief valves and filters ensured safe handling of corrosive gases, complying with HTM 02-01.
These examples show how safety features prevent disasters.
Emerging Trends in Safety Features
The manifold industry is innovating safety:
- IoT-Enabled Alarms: Remote alerts via apps.
- AI-Predictive Maintenance: Sensors predict failures.
- Eco-Friendly Materials: Non-fluoropolymer designs for safety and sustainability.
- Enhanced Purge Systems: Automatic purging for UHP gases.
- Integrated Gas Detection: Built-in sensors for leaks.
These trends make manifolds safer and smarter.
Practical Tips for Selecting Manifolds with Optimal Safety Features
- Assess Risks: Identify gas hazards to prioritize features (e.g., relief valves for high-pressure).
- Automation Level: Fully automatic for hospitals.
- Material: Stainless steel for corrosive gases.
- Supplier: Choose reputable brands like Pattons Medical or Middlesex Gases.
- Budget: Balance features with TCO.
Consult experts for tailored solutions.

Conclusion
Safety features are the cornerstone of gas changeover manifolds, ensuring reliable, uninterrupted gas supply while mitigating risks like leaks, over-pressure, and contamination. From automatic changeover and pressure relief valves to alarms and purge systems, these features protect lives and equipment in critical settings like hospitals. Compliance with standards like NFPA 99 and OSHA is essential, with maintenance ensuring long-term safety. As trends like IoT and AI advance, manifolds will become even safer. By understanding and prioritizing safety features, facilities can select manifolds that enhance operational reliability and compliance. Invest in a manifold with robust safety features today to safeguard your operations tomorrow.
For more about the safety features of gas changeover manifolds: ensuring operational safety, you can pay a visit to Jewellok at https://www.jewellok.com/ for more info.
Recent Posts
What is a Xenon (Xe) Ultra High Purity Gas Regulator?
Five Key Considerations When Choosing a TMA Gas Changeover Manifold
Tags
Recommended Products
-

768L Stainless Steel Male Tube Butt Weld Connector | Clean Weld Fittings And Ultra-High Purity Fittings
-

762L Stainless Steel High Purity Union High-Purity Gas System Fittings
-

Integrated Gas System (IGS) Modular Integrated Gas Systems (TMS) Integrated Gas Supply System For Semiconductor And Laboratory
-

Semi Automatic Oxygen Nitrogen Helium Argon Gas Changeover Manifold Manual Gas Changeover Manifold Panel For Gas Cylinders
-

763L Stainless Steel High Purity Pressure Reducing Union Fittings And Tubing Pressure Reducing Valve Adjustment
-
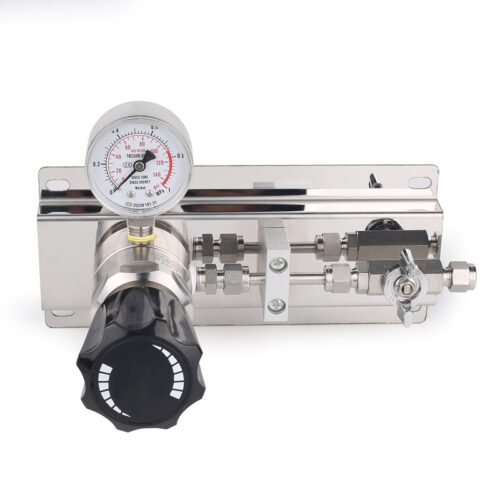

High Purity Gas Cylinder Semi Automatic Changeover Manifold Regulator Panel 3000psig Stainless Steel Gas Control Panel 1/8 Npt With Gauge
-

Manual Gas Rack High Purity Gas Delivery Systems JW-100-GR
-
T-BOX JW-TB-C Special Gas Delivery System Gas Valve Manifold Boxes