Blog
Jewellok is a professional pressure regulator and valve manufacturer and supplier.
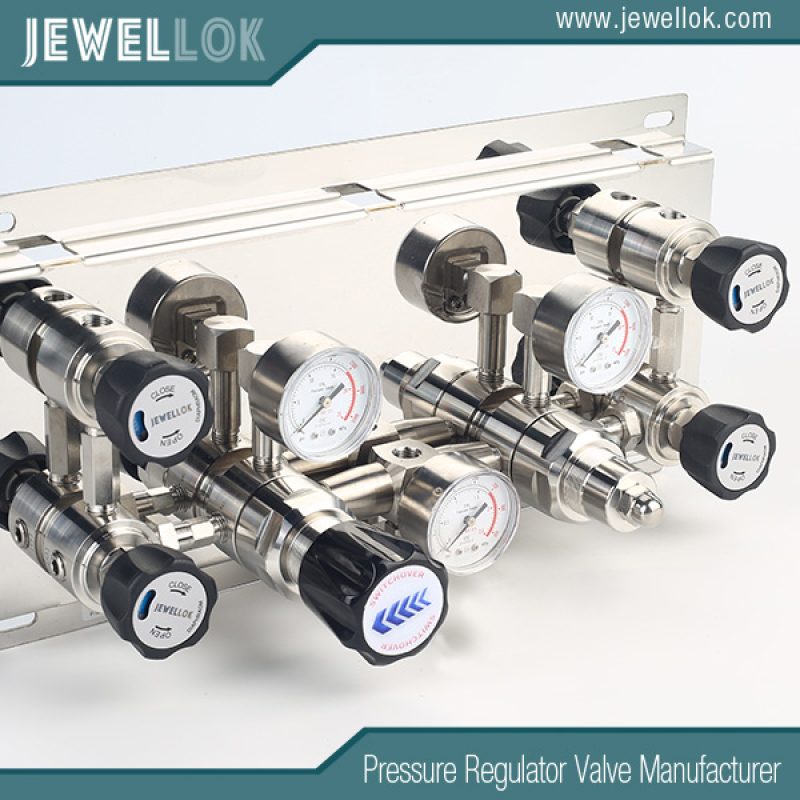

The Secret to Boosting Productivity:Gas Changeover Manifold for Industrial Applications
- Pressure Regulator Valve Manufacturer
- argon gas changeover manifold, argon gas changeover manifold supplier, argon gas changeover manifold supplier philippines, Auto Gas Changeover Manifold System, Automatic gas changeover manifold, automatic gas cylinder changeover system, best gas changeover manifold, Best gas changeover manifold for laboratories, best gas changeover manifold philippines, best gas changeover manifold supplier, best gas changeover manifold supplier philippines, BURSAN Gas Changeover Manifold, CO2 gas changeover manifold, Components of a gas changeover manifold, gas changeover manifold, Gas changeover manifold design, Gas changeover manifold for cleanroom, gas changeover manifold for hospital, Gas changeover manifold for industrial applications, gas changeover manifold for laboratories, Gas changeover manifold for manufacturing, Gas changeover manifold for welding, gas changeover manifold India, Gas changeover manifold installation guide, Gas Changeover Manifold Maintenance, Gas cylinder changeover system, Gas manifold pressure regulator system, gas regulator manifold, High-pressure gas manifold, Medical gas manifold, Safety features of gas changeover manifolds
- No Comments
The Secret to Boosting Productivity:Gas Changeover Manifold for Industrial Applications
In industrial environments where a continuous and reliable supply of gases is essential, gas changeover manifolds play a pivotal role. These systems are designed to automatically switch between multiple gas sources, such as cylinders or tanks, ensuring uninterrupted flow when one source depletes. This is particularly critical in sectors like manufacturing, chemical processing, welding, laboratories, and energy production, where even brief interruptions can lead to production downtime, safety hazards, or quality issues. As industries increasingly rely on gases like nitrogen, argon, hydrogen, oxygen, and CO2 for processes ranging from welding to inerting and purging, the demand for efficient and safe gas changeover manifolds has grown significantly.
The global market for gas manifolds, including changeover systems, is expanding due to advancements in automation, safety regulations, and the rise of industries like renewable energy and semiconductors. According to market analyses, the gas manifold market is driven by the need for enhanced safety and efficiency, with automatic systems reducing manual intervention and minimizing risks. In this 2000-word article, we will explore what gas changeover manifolds are, how they work, their types, components, industrial applications, benefits, safety features, installation, maintenance, regulatory standards, emerging trends, and practical tips for selection. This guide aims to help engineers, facility managers, and procurement specialists understand and implement these systems effectively for optimal industrial performance.

What Is a Gas Changeover Manifold?
A gas changeover manifold is a centralized distribution system that connects multiple gas cylinders or tanks to a single outlet line, allowing for automatic or manual switching between sources to maintain a continuous gas supply. It monitors the pressure in the active (primary) gas bank and switches to the reserve bank when the primary depletes, without interrupting the flow to downstream equipment. This seamless transition is vital in industrial applications where gas is used for processes like welding, cutting, inerting, or chemical reactions.
Manifolds are typically installed in gas storage rooms or near usage points, connected via high-pressure hoses (pigtails) to cylinders. They can handle various gases, from inert (nitrogen, argon) to flammable (hydrogen, acetylene) or corrosive (chlorine), with designs tailored to gas properties. In industrial settings, manifolds reduce cylinder change frequency, enhance safety by minimizing manual handling, and optimize gas usage by ensuring full depletion of cylinders.
The concept of gas manifolds evolved from simple manual valve setups in the early 20th century to sophisticated automatic systems in the 1980s, driven by industrial automation and safety needs. Today, they are integral to operations in factories, refineries, and labs, where reliability is paramount.
How Does a Gas Changeover Manifold Work?
The operation of a gas changeover manifold is based on pressure monitoring and valve switching to ensure uninterrupted gas flow. Here’s a step-by-step explanation:
- Initial Setup: Cylinders are grouped into banks (primary and reserve), connected via pigtails with check valves to prevent backflow. The manifold is configured to draw from the primary bank first.
- Normal Operation: Gas flows from the primary bank through inlet valves, pressure regulators (to reduce high cylinder pressure to usable levels), and the outlet to equipment. Pressure sensors monitor levels continuously.
- Low-Pressure Detection: As the primary bank depletes, pressure drops. When it reaches a preset threshold (e.g., 50-100 psi), sensors detect the change and signal the control unit.
- Automatic Switching: The changeover valve (solenoid or mechanical) activates, redirecting flow to the reserve bank. This happens seamlessly, with no interruption.
- Alarm and Notification: Alarms (audible, visual, or digital) alert operators to replace the empty bank. Advanced systems send SMS or email notifications.
- Reset and Continuation: After replacing cylinders, operators reset the system, swapping primary and reserve designations. The cycle repeats.
- Safety Integration: Relief valves vent excess pressure, filters remove impurities, and check valves prevent mixing.
In manual manifolds, operators monitor gauges and switch valves, while semi-automatic versions switch automatically but require manual reset.
Fully automatic systems handle everything electronically.
Types of Gas Changeover Manifolds
Manifolds vary based on automation, capacity, and application:
1.Manual Changeover Manifolds:
-
- Description: Basic systems with manual valves and gauges.
- Features: Low cost, simple design.
- Applications: Small workshops or low-demand industries.
- Advantages: Affordable, easy to maintain.
- Disadvantages: Labor-intensive, risk of downtime.
2. Semi-Automatic Changeover Manifolds:
-
- Description: Automatic switching with manual reset.
- Features: Pressure switches, alarms.
- Applications: Medium-scale manufacturing, welding.
- Advantages: Reduces monitoring, quick response.
- Disadvantages: Still requires intervention.
3. Fully Automatic Changeover Manifolds:
-
-
- Description: Complete automation with electronic controls.
- Features: Digital displays, remote monitoring.
- Applications: Chemical plants, semiconductors.
- Advantages: Continuous supply, minimal error.
- Disadvantages: Higher cost, power-dependent.
-
4. High-Pressure vs. Low-Pressure:
-
- High-Pressure: For gases like hydrogen (up to 3000 psi).
- Low-Pressure: For CO2 or air (up to 500 psi).
5. Wall-Mounted vs. Floor-Standing:
-
- Wall-Mounted: Space-saving for compact facilities.
- Floor-Standing: For large cylinder banks.
Selection depends on gas type, demand, and budget.
Components of a Gas Changeover Manifold
A typical industrial manifold includes:
- Cylinder Headers: Connect multiple cylinders in a bank.
- Pigtails: Flexible hoses with check valves.
- Isolation Valves: For cylinder replacement.
- Pressure Transducers: For monitoring.
- Changeover Unit: Solenoid valve for switching.
- Regulators: Maintain outlet pressure.
- Control Panel: With alarms and indicators.
- Safety Relief Valves: Vent excess pressure.
- Filters: For purity maintenance.
Materials like stainless steel ensure corrosion resistance.
Applications of Gas Changeover Manifolds in Industrial Settings
Manifolds are used in:
- Welding and Metal Fabrication: For continuous argon or CO2 supply, preventing weld defects.
- Chemical Processing: For inert gases like nitrogen in reactors.
- Semiconductors: For UHP gases like silane in fabrication.
- Food and Beverage: For CO2 in carbonation.
- Pharmaceuticals: For sterile gases in production.
- Hydrogen Energy: For high-pressure hydrogen in fuel cells.
- Laboratories: For analytical gases like helium.
These applications demonstrate manifolds’ versatility.
Benefits of Gas Changeover Manifolds
Manifolds offer:
- Continuous Supply: No downtime during cylinder changes.
- Safety: Reduce manual handling risks, prevent leaks.
- Efficiency: Automate processes, optimize gas use.
- Cost Savings: Minimize labor and gas waste.
- Compliance: Meet safety standards.
- Scalability: Expandable for growing needs.
In industrial settings, they enhance productivity.
Safety Features of Gas Changeover Manifolds
Safety is integral:
- Automatic Switching: Prevents supply failure.
- Relief Valves: Vent excess pressure.
- Check Valves: Prevent backflow.
- Alarms: Notify of low pressure.
- Filters: Remove impurities.
- Isolation Valves: For safe maintenance.
These features mitigate risks like leaks or over-pressure.
Installation of Gas Changeover Manifolds
Installation steps:
- Site Selection: Ventilated, secure area.
- Mounting: Secure to walls or floors.
- Cylinder Connection: Use pigtails with check valves.
- Piping: Connect outlet with regulators.
- Electrical Setup: For automatic systems.
- Testing: Pressure and leak tests.
Professional installation ensures compliance.
Maintenance of Gas Changeover Manifolds
Maintenance practices:
- Daily: Check gauges and alarms.
- Weekly: Inspect pigtails and valves.
- Monthly: Test switching and clean filters.
- Annual: Calibrate sensors, pressure test.
Regular maintenance prevents failures.
Regulatory Standards for Gas Changeover Manifolds
Standards include:
- NFPA 55: For compressed gases, requiring relief valves and alarms.
- CGA P-1: Safe handling guidelines.
- ASME B31.3: Piping design.
- OSHA 1910.101: Compressed gas safety.
- ISO 7396: For medical gases.
Compliance is mandatory for safety.
Emerging Trends in Gas Changeover Manifolds
Trends include:
- IoT Integration: Remote monitoring.
- High-Purity Designs: For semiconductors.
- Sustainability: Eco-friendly materials.
- Automation Enhancements: AI for predictive maintenance.
- Modular Systems: Easy expansion.
These trends drive innovation.
Practical Tips for Selecting a Gas Changeover Manifold
Tips:
- Assess Gas Demand: Calculate flow and pressure.
- Automation: Fully automatic for high-demand.
- Material: Stainless steel for corrosive gases.
- Supplier: Reputable like Swagelok.
- Budget: Consider TCO.
Case Studies
- Chemical Plant (USA): Automatic manifold reduced downtime by 90%.
- Manufacturing Facility (Germany): Semi-automatic system improved safety.
- Solar Plant (India): Manifold ensured continuous gas supply.

Conclusion
Gas changeover manifolds are indispensable for industrial applications, ensuring continuous gas supply while prioritizing safety. From automatic switching and relief valves to alarms and filters, their safety features mitigate risks and enhance reliability. Proper installation, maintenance, and compliance with standards like NFPA and CGA are crucial. As trends like IoT and sustainability evolve, manifolds will become even more efficient. By selecting the right manifold based on gas type, demand, and budget, industries can optimize operations. Invest in a quality gas changeover manifold to safeguard your processes and ensure seamless performance.
For more about the secret to boosting productivity:gas changeover manifold for industrial applications, you can pay a visit to Jewellok at https://www.jewellok.com/ for more info.
Recent Posts
What is a Xenon (Xe) Ultra High Purity Gas Regulator?
Five Key Considerations When Choosing a TMA Gas Changeover Manifold
Tags
Recommended Products
-

767LP Port Connector Ultra High Purity VCR Metal Gasket Face Seal Tube Fittings
-
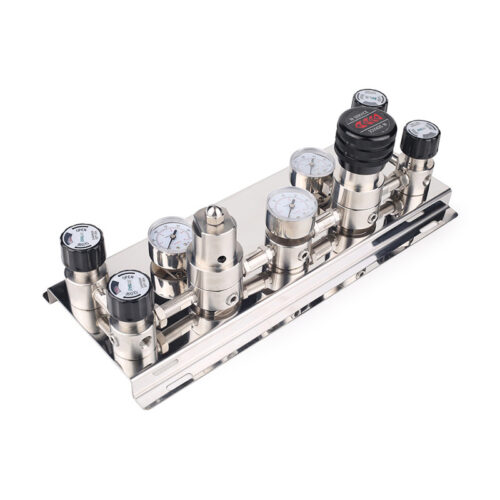

Stainless Steel High Pressure Specialty Gas Changeover Manifold For High Purity Oxygen Nitrogen Argon Helium Hydrogen Co2
-

Specialty Gas Valves Ultra High Purity Gas Valves Ultra High Purity Gas Cylinder Valves UHP Cylinder Valve Ultra High Purity Gas Regulator
-

775L Bulkhead Reducing Union | Stainless Steel High Purity Double Ferrule Bulkhead Reducing Unions
-
FT-BOX JW-FTB-C Valve Manifold Panels And Boxes With High Purity Configurable Systems
-

7102L Stainless Steel 316L SS Union Cross Ultra High Purity Long Arm Union Elbow Tee Cross Butt Weld Fittings
-

Bulk Specialty Gas Systems (BSGS) Gas Cabinets And Scrubber Tail Gas Treatment Cabinets For High Purity Bulk Specialty Gas Delivery
-
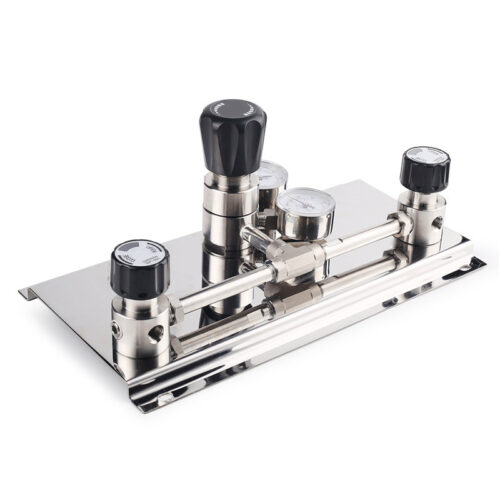

High Purity Semi-Auto Stainless Steel Changeover Manifold System, Nitrogen High Pressure Control Panel With Semiconductor Valve Manifold Box Diaphragm Valves